OXFORD STREET RENOVATION
Residential Land Development Management
London, United Kingdom
Sep 2021 – Mar 2022
Category: City Renovation, Computational Design
Featured in: AA EmTech Project Review 2021/2022
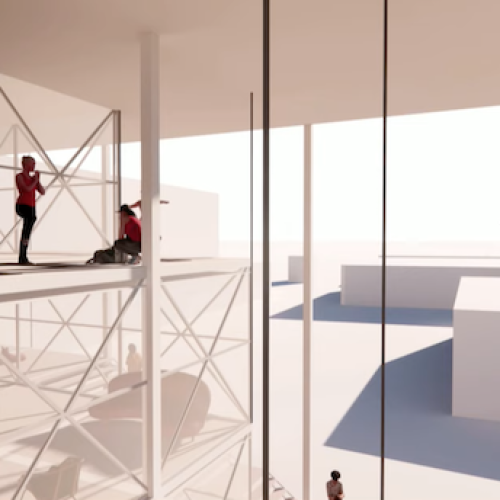
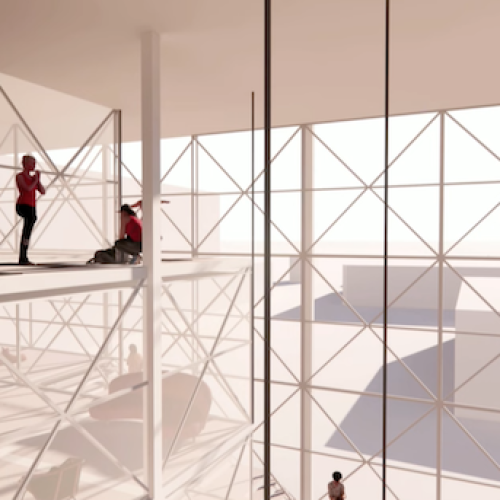
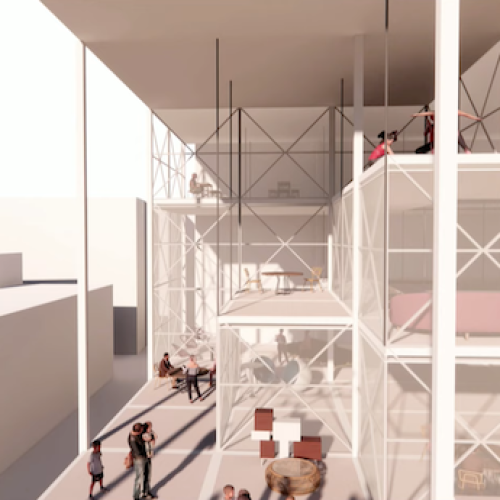
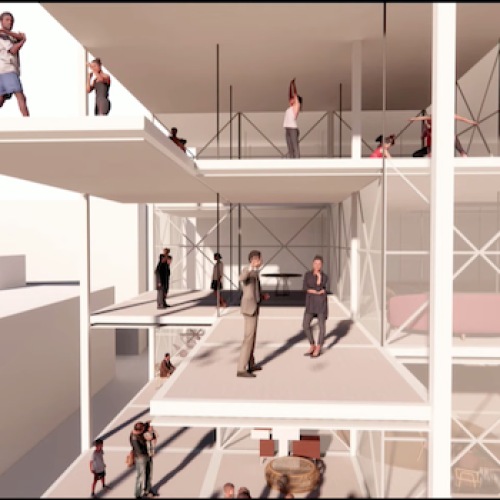
The computational architecture design project for Oxford Street epitomizes a holistic approach to urban revitalization, integrating cutting-edge technology with user-centric design principles to create a flexible and adaptive urban landscape. While further refinement and prototyping are warranted, the project lays a robust foundation for the development of adaptable urban environments that can thrive amidst rapid societal and technological change.
- Integrate and analyze vast datasets, including Google Place API data
- identify optimal pathways for integrating new spaces within the Oxford Street district, enhancing connectivity and accessibility while promoting pedestrian activity
- tailor spatial configurations to specific functions and user requirements, fostering adaptability and flexibility within the urban environment
- facilitate a balanced distribution of functions throughout the district, enhancing social cohesion and vibrancy while mitigating underutilized spaces
BACKGROUND
Recent observations indicate a decline in foot traffic along Oxford Street, reflected in a reduction in the Passenger Index from 155 in 2016 to 78 in 2020. This decline is mirrored by an increase in vacancy rates across retail, office, and housing sectors. To safeguard Oxford Street’s role as a vibrant social hub amidst changing societal dynamics, a systemic approach to adaptability is proposed. This approach entails the redistribution of functions at an urban scale and the facilitation of various spatial configurations at an architectural scale, tailored to accommodate evolving needs.
EXPERIMENT 1 : PATHWAY OPTIMIZATION
Objective: Identify the most suitable pathways for integrating new spaces within the Oxford Street district.
Methodology: Utilizes a multi-objective algorithm considering factors such as street vibrancy, pedestrian comfort, and solar exposure.
Outcome: Determination of optimal pathways connecting activated and underutilized areas.
Data analysis utilizing Google Place API has been employed to gauge the activity levels of different areas within Oxford Street. Furthermore, an automated system has been devised to streamline the design process, focusing initially on identifying optimal pathways for integrating new spaces. Through a multi-objective algorithm considering factors such as street vibrancy, pedestrian comfort, and solar exposure, suitable pathways linking activated and underutilized areas are delineated.
EXPERIMENT 2 : SPATIAL CONFIGURATION
Objective: Allocate specific functions along identified pathways, focusing on social and cultural amenities.
Methodology: Employ a combination of automated algorithms and manual adjustments to tailor spatial configurations.
Outcome: Customized spatial arrangements optimized for functionality and flexibility.
Utilizing a combination of automated algorithms and manual adjustments, spatial configurations are tailored to optimize functionality while maintaining flexibility. Crowd simulations are conducted to assess the impact of these interventions on pedestrian movement patterns, ensuring a balanced distribution of activity throughout the district.
EXPERIMENT 3: CROWD SIMULATION AND FUNCTIONAL DISTRIBUTION
Objective: Assess the impact of spatial interventions on pedestrian movement patterns and distribute functions accordingly.
Methodology: Conduct crowd simulations to evaluate the distribution of activity and refine spatial allocations.
Outcome: Balanced distribution of functions throughout the Oxford Street district to enhance social cohesion and vibrancy.
In parallel, environmental criteria including sun exposure, views, and sound are integrated into the design process to enhance user experience and comfort. The resulting adaptable system comprises movable slab and partition systems, affording users the ability to customize spatial configurations according to their needs. This bottom-up approach, rooted in real-time data and user feedback, represents a departure from traditional top-down urban planning paradigms, fostering a dynamic and responsive urban environment capable of meeting the evolving demands of contemporary society.