Arctic Sustainability
Integrating Design for Resilient Residential Development
Feb 2021 – Mar 2021
Category: Town Planning, Computational Design
Director: Michael Weinstock
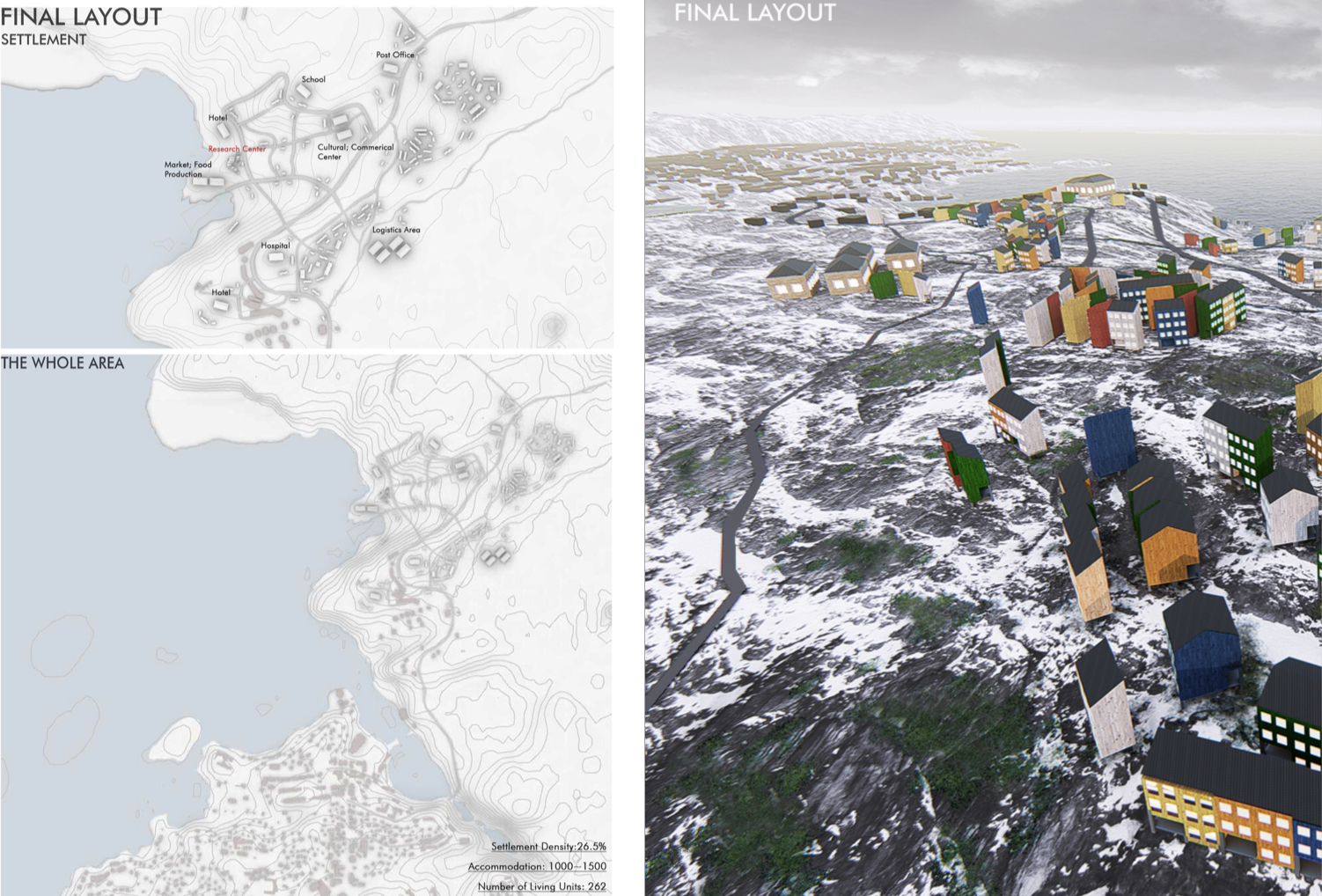
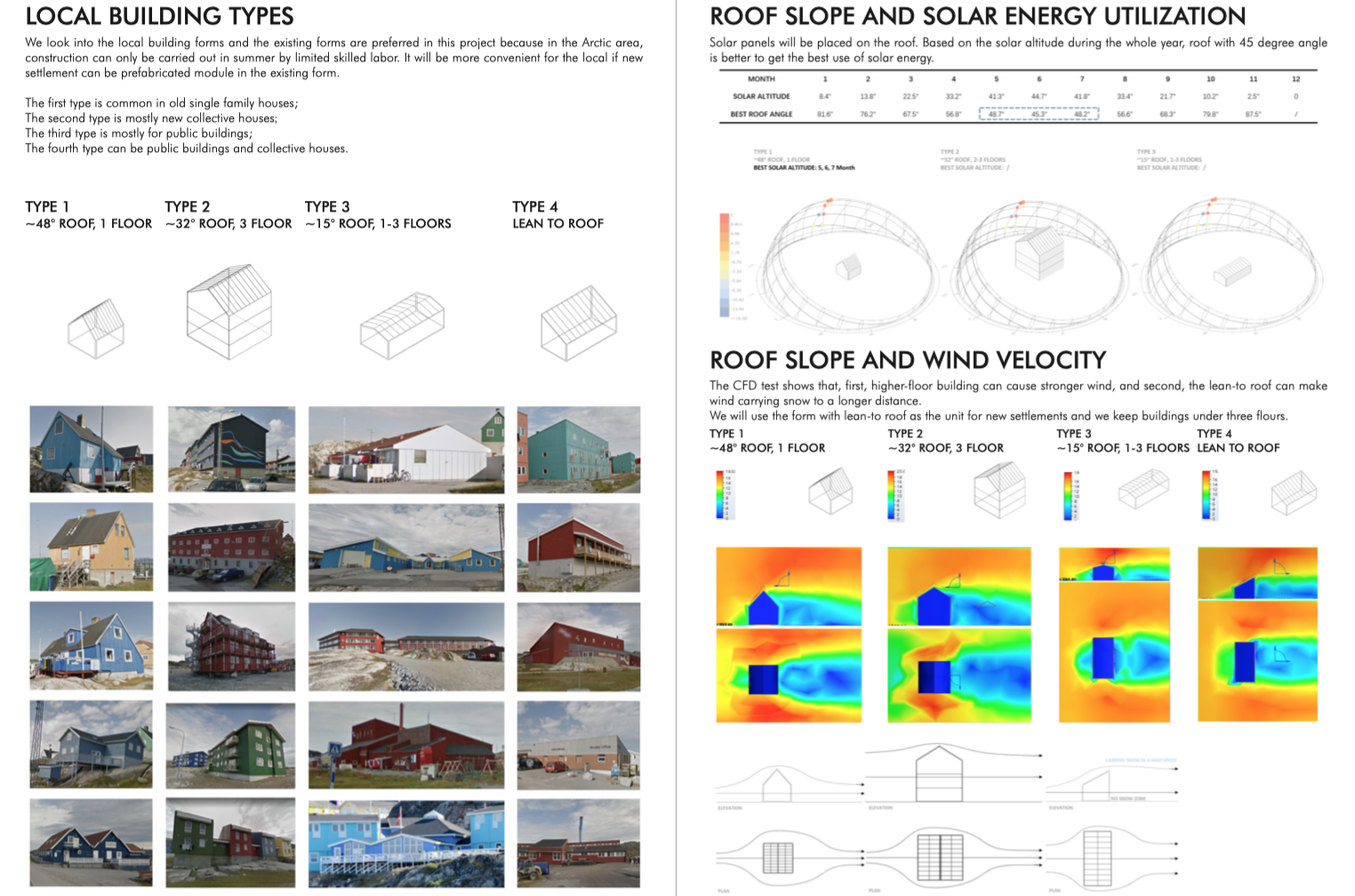
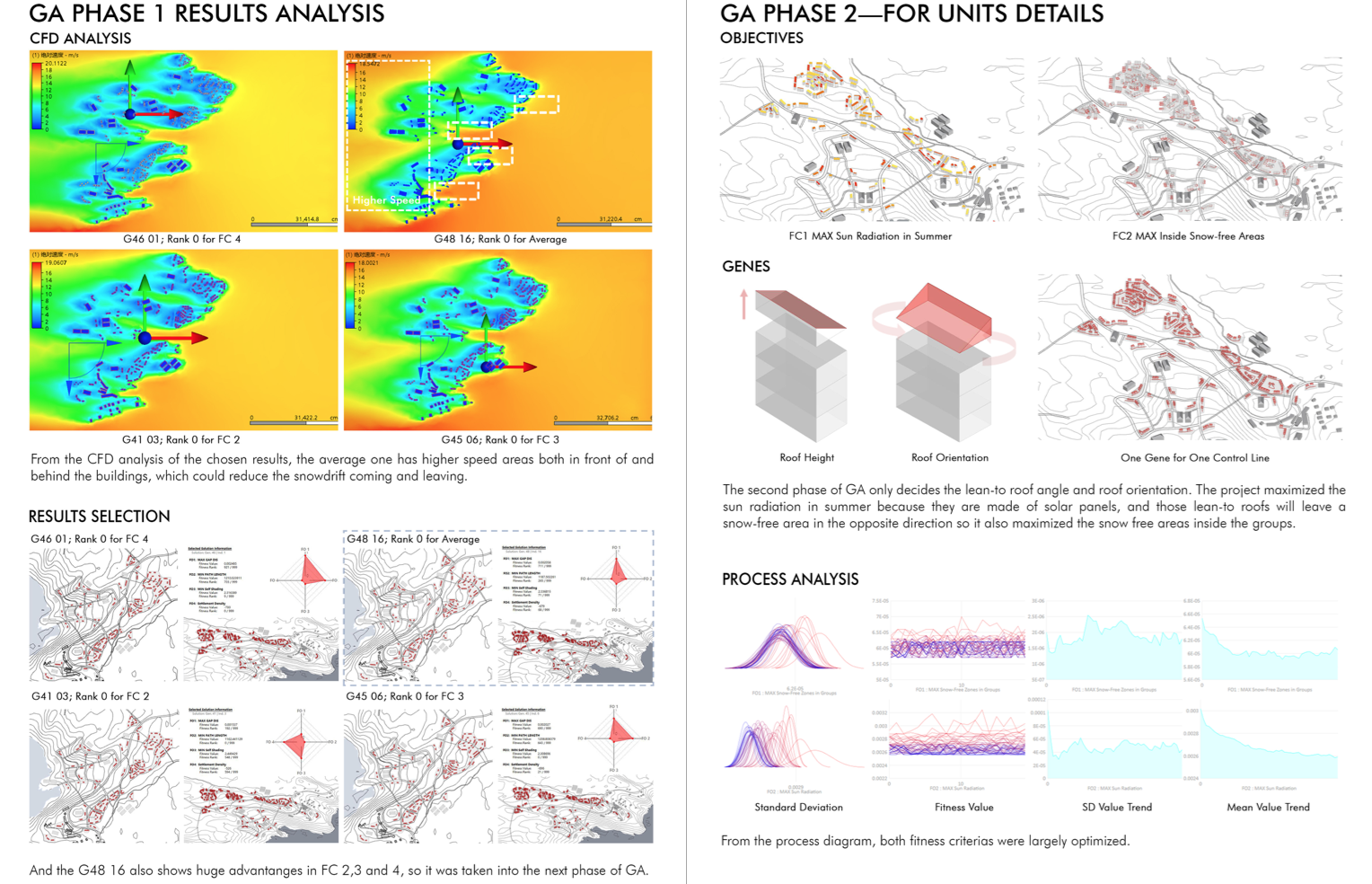

The Arctic region presents unique challenges and opportunities for residential development, necessitating innovative approaches to ensure sustainability and livability. The project focuses on crucial aspects such as residential area location, road network optimization, and architectural considerations. Focusing on the town of Ilulissat in Greenland, the project aims to harness local resources and environmental conditions to create resilient and energy-efficient residential areas conducive to human habitation.
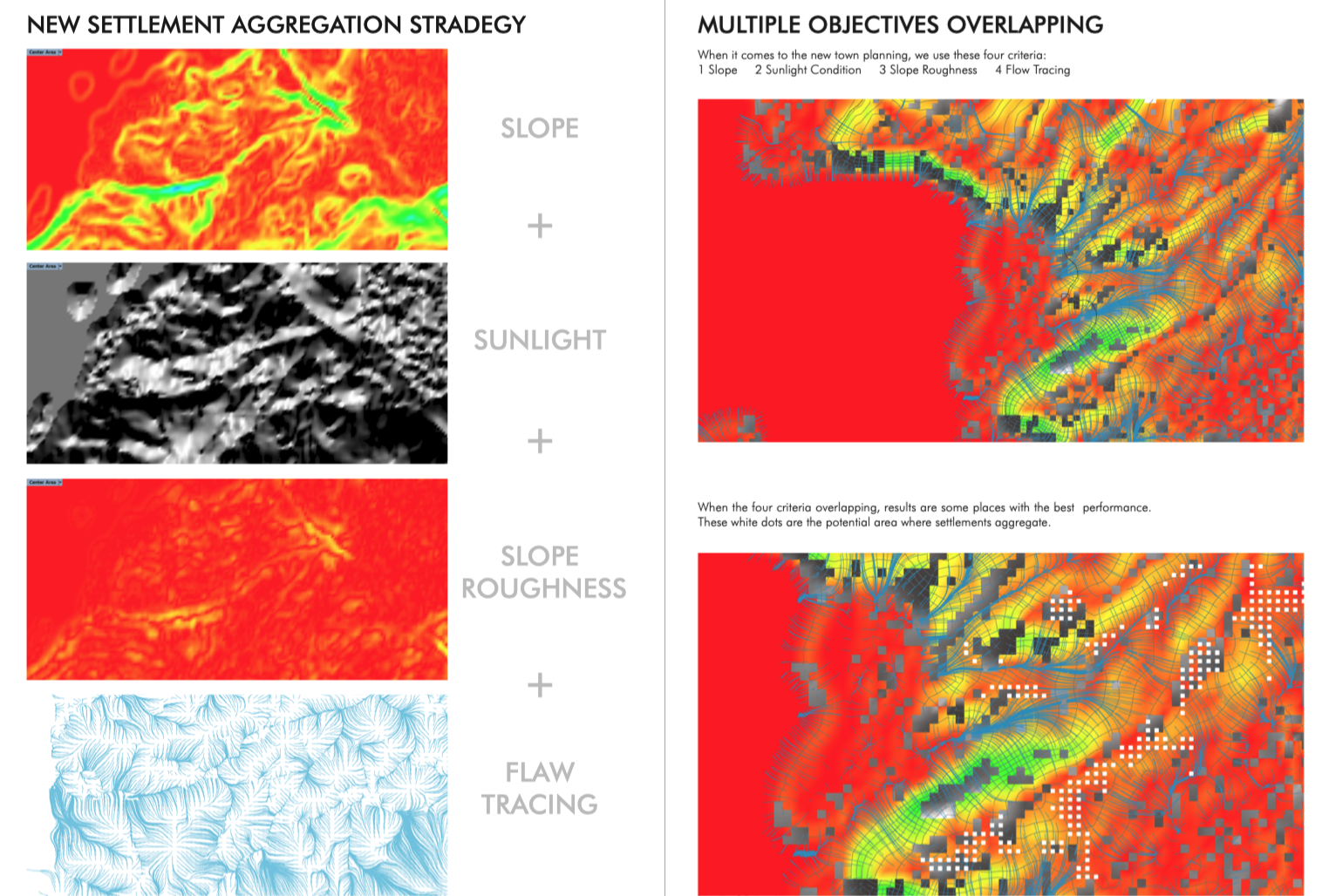
- The project identifies potential settlement sites through comprehensive analyses including terrain assessment, slope analysis, and site drainage evaluation.
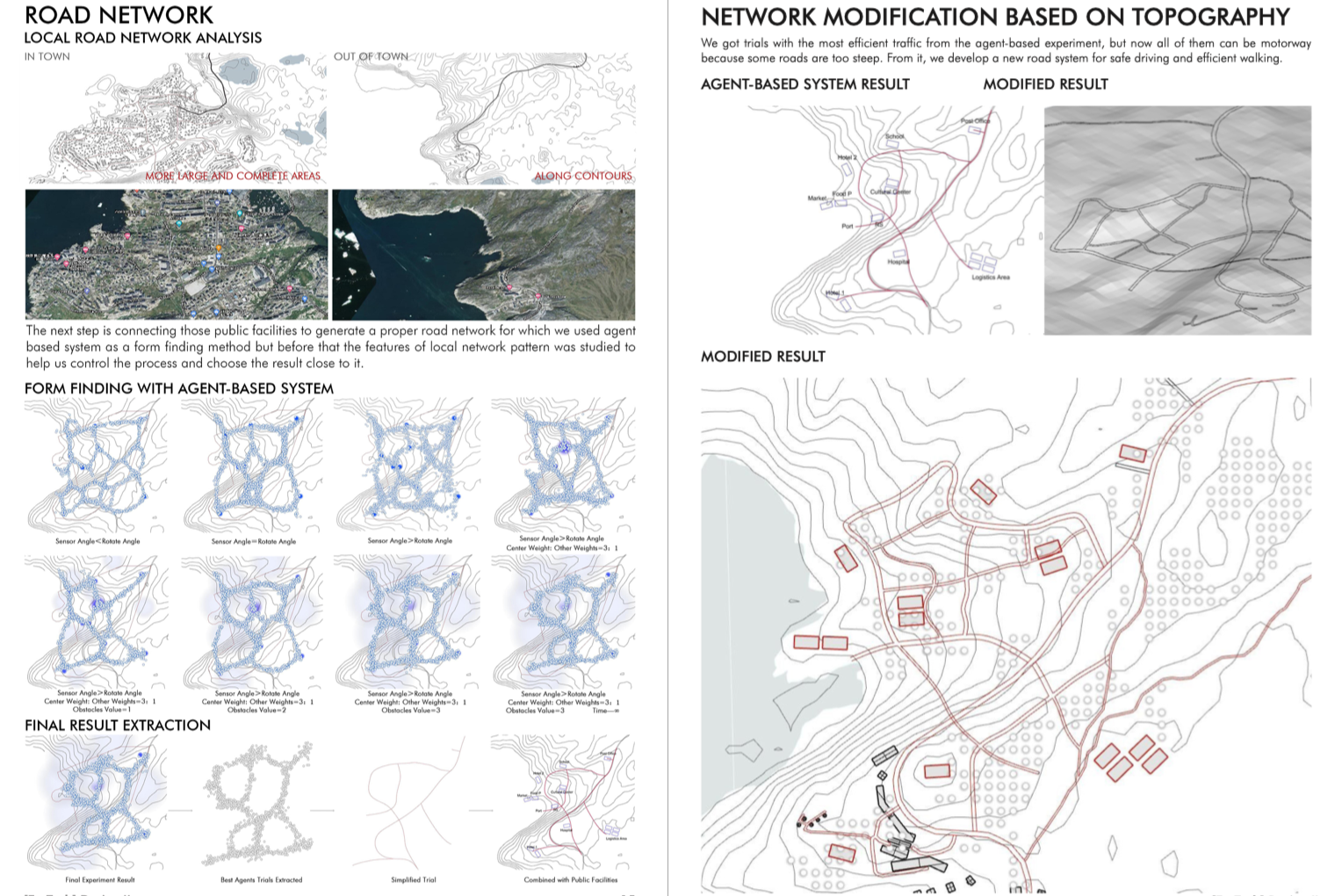
- Integrates innovative approaches for road networks to ensure efficient pedestrian connectivity and safe vehicular transit amidst challenging terrains.
- Architectural solutions incorporate hydrodynamics and solar energy utilization to optimize living conditions while minimizing environmental impact
Site Research and Computational Analysis
A cornerstone of the design proposal is the integration of site research and computational analysis to identify suitable locations for new residential developments. Through rigorous terrain and slope analysis, coupled with drainage assessments, potential settlement sites are discerned with a focus on optimizing environmental suitability and infrastructure feasibility. This data-driven approach ensures informed decision-making in the selection of sites, laying the foundation for sustainable community development.
Infrastructure and Road Network Optimization
Central to the project is the optimization of infrastructure, particularly road networks, to facilitate both pedestrian mobility and vehicular access. Leveraging computational techniques, the design endeavors to create an efficient and safe road network tailored to the region’s unique topography. Furthermore, considerations for tourism development drive modifications to enhance the driving experience, thereby fostering economic growth while ensuring environmental sustainability.
Architectural Innovation for Environmental Resilience
In response to the Arctic region’s extreme climate conditions, the project integrates architectural innovation aimed at enhancing environmental resilience and energy efficiency. By incorporating principles of hydrodynamics and solar energy utilization, the proposed housing designs seek to mitigate the impact of harsh winds and snow while maximizing the harnessing of solar energy. This holistic approach not only fosters comfortable living conditions but also reduces reliance on traditional energy sources, aligning with broader environmental conservation goals.
Community Integration and Public Space Design
Recognizing the importance of community integration and public space in Arctic living, the design prioritizes the creation of residential clusters with ample communal areas. Through careful consideration of terrain features, residential clusters are strategically positioned to foster social interaction and outdoor gatherings, particularly during the extended polar night period. This emphasis on community-centric design promotes social cohesion and enhances residents’ quality of life amidst challenging environmental conditions.